1
Key Stage 3 PE Revision and Work Booklets
Contents
Contents
Lesson/Resource
Page
Numbers
Tick when
complete
Lesson 1 – Warm ups, cool downs and
the components of fitness
2 - 6
Lesson 2 – Fitness Testing
7 - 11
Lesson 3 – Training Methods
12 - 15
Lesson 4 - Short and long term effects of
exercise
16
Lesson 5 – Maximum Heart Rate (MHR)
17
Lesson 6 – Components of the heart
18 - 19
Lesson 7 – Structure and function of the
muscular system
20 - 22
Lesson 8 – Structure of the skeletal
system
23 - 24

2
Lesson 1
Warm Up
There are 5 key components of the warm up:
1. Pulse raiser – This is light exercise that slowly increases the heart rate and
gradually increases body temperature. For example, jogging, skipping and cycling.
2. Mobility – Exercises that take the joints through their full movement. For
example, arm swings, hip circles, open and close the gates.
3. Stretching – This can include dynamic or static stretches. Static stretches are
when the body remains still for example touching your toes. Dynamic stretching
are stretches whilst moving for example lunges.
4. Dynamic movements – Movements that show a change of speed and direction
e.g. shuttle runs.
5. Skill rehearsal – This involves practicing common skills that would be used in the
activity e.g. dribbling drills for football.
Stretching Pulse raising Skill rehearsal
Benefits of a warm up
Warm-up raises your body temperature. Dynamic warm-up exercises raise your body
temperature by heating up your muscles. ...
Warm-up enhances muscle performance. ...
Warm-up boosts heart function. ...
Warm-up improves the load distribution in your joints. ...
Warm-up prevents injuries.
Cool down
The key components of a warm down are:
1. Low intensity exercises such as light running or jogging. The aim is to gradually lower the heart rate and
reduce body temperature.
2. Stretching – This would be static stretches held for up to 30 seconds each.
Why is a cool down important?
Cooling down helps recovery by stretching the muscles and reducing risk of damage to joints.
Helps to remove waste products such as Lactic acid.
Reduces the risk of muscles cramps and soreness.

3
Components of Fitness
Physical
Component of Fitness
Definition
Aerobic Endurance
The ability to work the whole body
for a long period of time without
tiring.
Muscular Endurance
The ability to repeat muscle
contractions over a long time without
tiring.
Strength
The amount of force a muscle can
exert against a resistance.
Speed
The time taken to perform a
particular action or cover a particular
distance.
Flexibility
The range of movement possible at a
joint
Body Composition
The percentages of fat, bone, water
and muscle in human bodies.
Skill
Component of Fitness
Definition
Balance
The ability to maintain a position or
posture without falling over.
Co-ordination
The ability to use two of more body
parts together.
Reaction time
The time taken to respond to a
stimulus.
Agility
The ability to change direction
quickly.
Power
The ability to perform strength
actions quickly.
4
Component of Fitness examples within sport
Component of Fitness
Example in Sport
Aerobic Endurance
Having good aerobic endurance fitness is
important for a rugby player to play the full
rugby match
Muscular endurance
Muscular endurance is important for a
marathon runner so that his muscles don’t tire
quickly when running
Strength
A shot putter will need to have good strength
to throw the shotput
Speed
A sprinter will need good speed within a 100 m
race
Flexibility
A gymnast would need good flexibility in order
to perform the splits
Body Composition
There are 3 body types:
Ectomorph
Endomorph
Mesomorph
Balance
A gymnast would need to have good balance
when performing a hand stand
Co-ordination
A tennis player would need co-ordination to
run and hit the ball
Reaction time
A sprinter needs good reaction time at the
start of a race to react to the gun
Agility
A footballer would need good agility to change
direction quickly when dribbling past a
defender
Power
Power is need in the legs when jumping up to
head the ball
https://www.nhsinform.scot/healthy-living/keeping-active/before-and-after-
exercise/warm-up-and-cool-down
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zxd4wxs/revision/2
5
Complete the table below using different sporting examples.
Component of Fitness
Example in Sport
Aerobic Endurance
An example of aerobic endurance in sport is
Mo Farrah completing the 10000 metres in the
Olympic games.
Another example is Lionel Messi running or
sprinting continuously throughout a football
match to receive the ball or while dribbling
with the ball.
Muscular endurance
Strength
Speed
Flexibility
Body Composition
Research and give definitions of each
body type.
Balance
Co-ordination
Reaction time
Agility
Power
6
Complete the Following Tasks
1. What are the 5 components of a warm up?
________________________________
________________________________
________________________________
________________________________
________________________________
2. Why is a cool down important?
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
3. Fill in the missing boxes:
Physical
Component of Fitness
Definition
Aerobic Endurance
The ability to repeat muscle
contractions over a long time without
tiring.
The amount of force a muscle can
exert against a resistance.
Speed
Flexibility
The percentages of fat, bone, water
and muscle in human bodies.
Skill
Component of Fitness
Definition
Balance
The ability to use two of more body
parts together.
Reaction time
Agility

11
You can research each of the above fitness tests using the following
links:
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zw7wmnb/revision/3
https://www.peresourcesbank.co.uk/wp-
content/uploads/2017/11/Knowledge-Organiser-GCSE-PE-Fitness-
Testing.pdf
https://www.teachpe.com/training-fitness/types-of-fitness-test
https://www.topendsports.com/testing/tests-popular.htm
Name the following fitness tests and the component of fitness it tests:
Name of fitness test_______________________________
Component of fitness______________________________

12
Name of fitness test________________________________
Component of fitness_______________________________
Name of fitness test_________________________________
Component of fitness________________________________
Lesson 3
Training Methods
There are a number of different ways of training that can improve health and fitness
necessary for a range of activities. Warming up and cooling down are essential parts of a
training session.
The different methods of training
All methods of training need to be specific to the individual performer, component of fitness and the
activity.
Continuous training develops cardiovascular fitness
A minimum of 20 minutes sub-maximal work.
Target heart rate range between 60% - 80% maximum heart rate (maxHR).
Swimming, running, cycling, walking or a combination of these disciplines.

13
Disadvantage - some participants find longer sessions to be boring.
Fartlek (speed play) training develops a range of components and is used by games players
A continuous form of training.
Changes in speed, incline and terrain are used to provide changes in exercise intensity.
Aerobic and anaerobic work can be done in the quantities that suit the performer.
Disadvantage - some urban areas have little variety of incline and terrain.
Interval training develops strength, speed and muscular endurance
Periods of intense work interspersed with timed rest.
A wide variety of fitness types can be developed.
Structured in reps and sets.
Intensity is measured by % maxHR.
Disadvantage - maximal nature of intervals can be too challenging for some participants.
Weight training develops strength
An interval form of training.
Intensity is measured in a percentage of the most weight a person can lift one time and is known
as % 1 REP MAX.
Time is structured in reps and sets with specific timings for recovery between sets.
Huge range of possible lifts combining machines, free weights and body weight exercises.
Disadvantage - many performers use poor technique while striving for an even heavier weight.
Plyometric training develops power
High intensity exercise involving explosive movements.
The muscle is lengthened and then rapidly shortened to develop the explosive capability
of the muscle.
Suitable for well-trained athletes.
Very effective for developing power.
Disadvantage - can cause injury if athlete is not in excellent condition.
Flexibility training develops flexibility
Essential training for all athletes in all sports and activities.
Time is measured by the length of hold and the recovery period between holds.
Intensity is measured as a percentage of range of motion (%ROM).
Disadvantage - underused by many athletes.
Circuit training
14
This develops muscular endurance, strength and/or cardiovascular fitness.
An interval form of training.
Stations are set out that train one or more components of fitness.
The performer moves from one station to the next with exercise periods and rest periods.
Circuits can be designed so that they are sport-specific.
Factors affecting training
The choice of how to train can be affected by many factors. Some training methods such as
weight training require the use of some specialist equipment whereas others such as
interval training do not. Therefore the availability of facilities is relevant.
Some training methods can also be very high impact and are less advisable for some groups
in society such as children or elderly people. Plyometrics is a very effective method of
developing explosive power but should not be used with a child that is growing or a
performer who is overweight or less fit. The high impacts can prove damaging to joints and
muscles unless the performer is in peak condition.
Training Method
Description
Component of Fitness
1. FARTLEK TRAINING
Involves exercising by varying
the time, distance, effort and
terrain. It usually involves a
mixture of running, jogging &
walking.
Aerobic Endurance
Muscular Endurance
2. INTERVAL TRAINING
Involves bursts of
exercise followed by periods
of rest or walking.
Aerobic Endurance
Muscular Endurance
3. CIRCUIT TRAINING
A series of different exercises
completed for a certain
amount of time, after one
another.
Aerobic Endurance
Muscular Endurance
Strength
4. WEIGHT LIFTING
Involves shifting weight to
increase the strength of
muscles using a programme of
repetitions and sets.
Muscular Endurance
Strength

15
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zchxnbk/revision/2
https://www.teachpe.com/training-fitness/training-methods
What are the following training methods and what components of fitness do
they train? (Remember, some training methods train more than one
component of fitness).
Training method__________________________________________________
Components of fitness_____________________________________________
5. CROSS TRAINING
Combines different methods
of training e.g. games,
aerobics and athletics and is
adaptable to a variety of
situations aiming to increase
overall performance.
Aerobic Endurance
Muscular Endurance
Strength
6. CONTINUOUS TRAINING
Involves exercising the body at
a moderate rate keeping the
pulse at a constant level
without periods of rest.
Aerobic Endurance
Muscular Endurance

16
Training method__________________________________________________
Components of fitness_____________________________________________
Training method__________________________________________________
Components of fitness_____________________________________________
Lesson 4
Short and Long Term Effects of Exercise
Short Term
Complete the missing answers below:
Respiratory System
Increased ___________________________________________
Increased production of _______________________________
Cardiovascular System
Raised ______________________________________________
Redistribution of _____________________________________
Other Effects

17
Raised _____________________________________________
Muscle _____________________________________________
Long Term
Respiratory System
___________________________
Cardiovascular System
___________________________
Muscular System
___________________________
Skeletal System
___________________________
Energy System
___________________________
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z9fhycw/revision/1
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z367tyc/revision/2
https://www.teachpe.com/anatomy-physiology/effects-of-exercise
Lesson 5
Maximum Heart Rate
Training is effective when it specifically targets the individual athlete. One way of achieving
this is by targeting the most relevant training threshold. For many athletes this involves
calculating a specific working heart rate.
Maximum heart rate = 220 – age
A 20-year-old athlete might want to calculate their maximum heart rate in order to
accurately calculate their training threshold:
Maximum heart rate = 220 – 20

18
Maximum heart rate = 200 beats per minute (BPM)
Calculate your MHR = _____________BPM
Measure your heart rate after completing the following
exercises and record them in the table below
Exercise
Beats Per Minute (BPM)
Resting Heart Rate (RHR)
1 minute press ups
1 minute burpees
1 minute sit ups
1 minute jogging on the
spot
1 minute plank
1 minute high knees
jogging on the spot
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/exercise-
intensity/art-20046887
https://www.polar.com/blog/calculate-maximum-heart-rate-running/
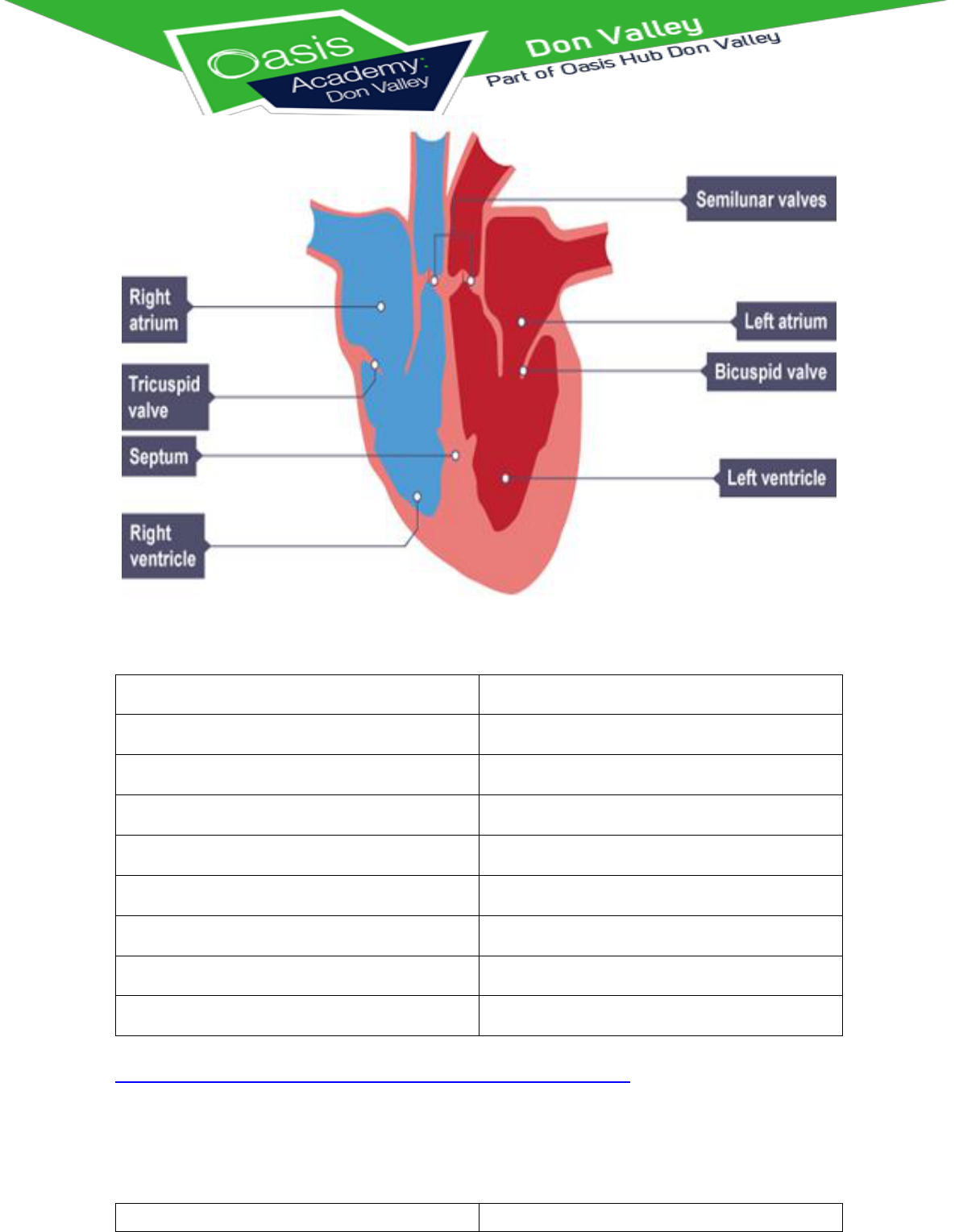
Lesson 6
Components of the Heart
19
Complete the following table:
Component of Heart
Function
Right Atrium
Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Septum
Semi-lunar Valve
Tricuspid Valve
Bicuspid Valve
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zrrry9q/revision/1
6. Name 8 components of the heart and their function.
Component of the heart
Function
22
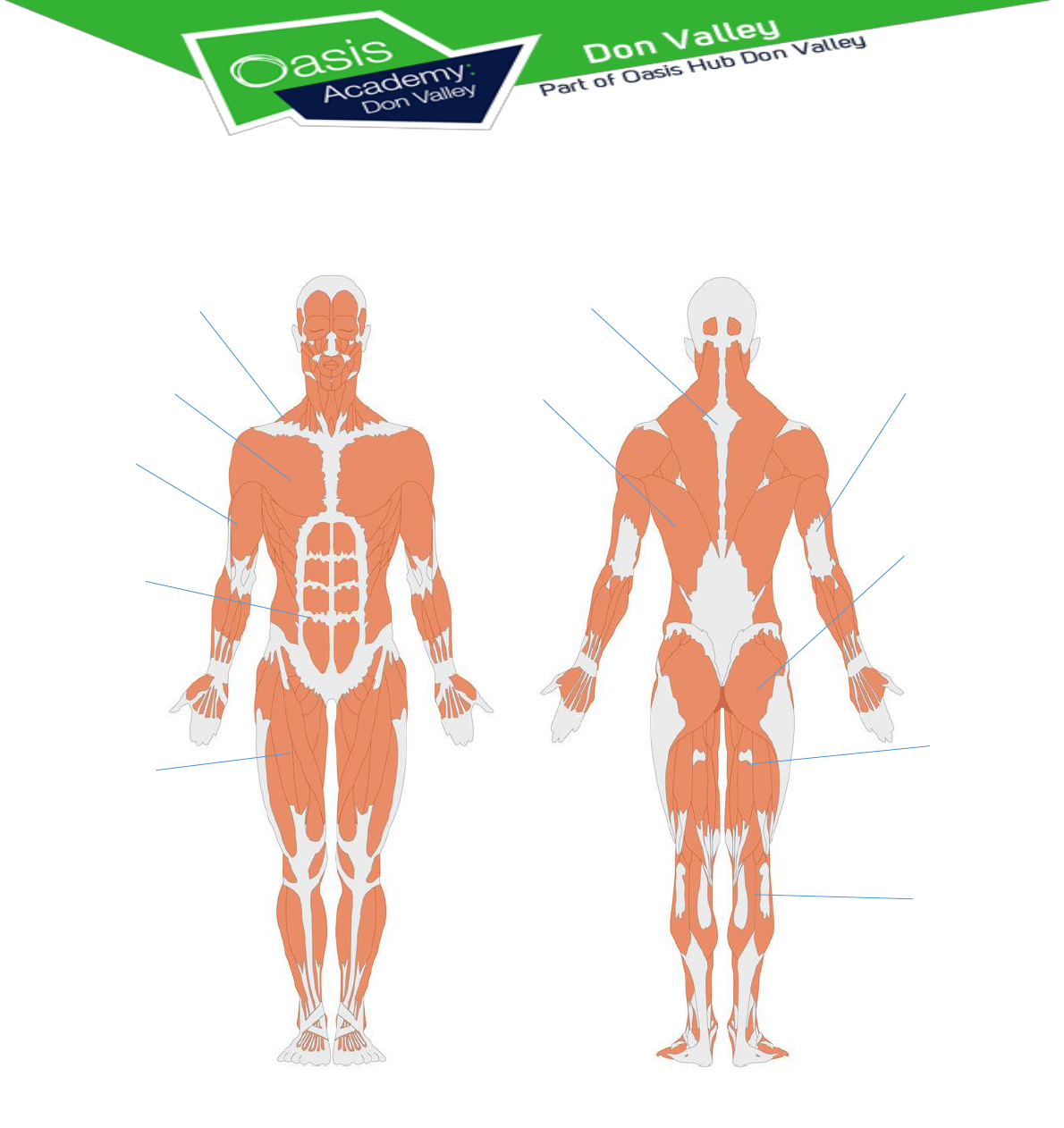
Muscle
Function
Deltoid
Trapezius
Muscle chiefly of the middle and
lower back that extends, adducts,
and rotates the arm medially and
draws the shoulder downward and
backward.
Pectorals
A muscle with two heads or points of
origin. The large muscle at the front
of the upper arm that flexes the
forearm.
Triceps
A large group of muscles in the front
of the abdomen that assists in the
regular breathing movement and
supports the muscles of the spine
while lifting and
keeping abdominal organs such as
the intestines in place.
Large fleshy muscle group covering
the front and sides of the thigh.
Hamstrings
Gluteals
The chief muscle of the calf of the
leg, which flexes the knee and foot. It
runs to the Achilles tendon from two
heads attached to the femur.
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zpkr82p/revision/2
Name the major muscles of the body and their function.
Major Muscle
Function
1.